Vulvodynia (vul-voe-DIN-e-uh) is chronic pain or discomfort around the opening of your vagina (vulva) for which there’s no identifiable cause and which lasts at least three months. The pain, burning or irritation associated with vulvodynia can make you so uncomfortable that sitting for long periods or having sex becomes unthinkable. The condition can last for months to years.
If you have vulvodynia, don’t let the absence of visible signs or embarrassment about discussing the symptoms keep you from seeking help. Treatment options are available to lessen your discomfort. And your doctor might be able to determine a cause for your vulvar pain, so it’s important to have an examination.
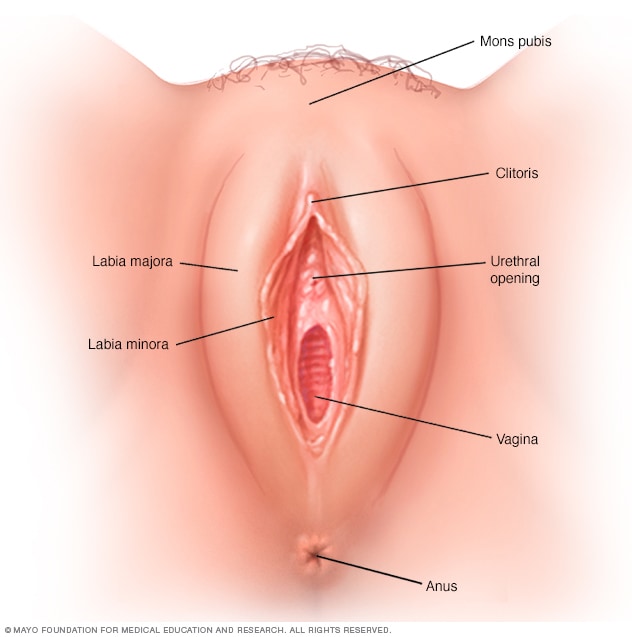
The main vulvodynia symptom is pain in your genital area, which can be characterized as:
Your pain might be constant or occasional. It might occur only when the sensitive area is touched (provoked). You might feel the pain in your entire vulvar area (generalized), or the pain might be localized to a certain area, such as the opening of your vagina (vestibule).
Vulvar tissue might look slightly inflamed or swollen. More often, your vulva appears normal.
A similar condition, vestibulodynia, causes pain only when pressure is applied to the area surrounding the entrance to your vagina.
Although women often don’t mention vulvodynia to their doctors, the condition is fairly common.
If you have pain in your genital area, discuss it with your doctor or ask for a referral to a gynecologist. It’s important to have your doctor rule out more easily treatable causes of vulvar pain — for instance, yeast or bacterial infections, herpes, precancerous skin conditions, genitourinary syndrome of menopause, and medical problems such as diabetes.
It’s also important not to repeatedly use over-the-counter treatments for yeast infections without seeing your doctor. Once your doctor has evaluated your symptoms, he or she can recommend treatments or ways to help you manage your pain
Doctors don’t know what causes vulvodynia, but possible contributing factors include:
Because it can be painful and frustrating and can keep you from wanting sex, vulvodynia can cause emotional problems. For example, fear of having sex can cause spasms in the muscles around your vagina (vaginismus). Other complications might include: